ผศ.พญ.ส ว ชา อ ศราด ส ยก ล แก วศ ร
|
|
|
- Ami Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Common Disorders of Hearing and Balance ผศ.พญ.ส ว ชา อ ศราด ส ยก ล แก วศ ร หน วยโสตประสาท ภาคว ชาโสต ศอ นาส กว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม กระบวนว ชา พ.วพ.306 (330306): ระบบประสาท 2 26 พฤศจ กายน 2557
2 ว ตถ ประสงค เพ อให น กศ กษาสามารถ 1. ม ความร ความเข าใจเก ยวก บพยาธ สภาพและพยาธ กาเน ด ของโรคท พบบ อยในระบบการได ย นและการทรงต ว 2. อธ บายพยาธ สร รว ทยาของโรคท พบบ อยในระบบการได ย น และการทรงต ว 3. อธ บายสาเหต และหล กการว น จฉ ยโรคท พบบ อยในระบบการ ได ย นและการทรงต ว 2
3 เน อหา Overview of anatomy of the hearing and balance system Common Hearing and Balance Disorders of the External ear/ Middle ear/ Inner ear Pathology/ Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology/ Etiology/ Principle for diagnosis ระด บของความผ ดปกต ของการได ย นและความสามารถในการฟ ง 3
4 Anatomy of the hearing and balance system
5 Ear: 3 parts 5
6 Pinna (auricle) 6
7 Middle ear 7
8 Inner ear Balance peripheral vestibular system Hearing peripheral auditory system 8
9 Peripheral auditory system: cochlea Organ of Corti 9 %20Organ%20of%20Corti.htm
10 Organ of Corti 10
11 Peripheral vestibular system 5 sensory organs 3 semicircular canals utricle, saccule 11
12 Angular acceleration 3 Semicircular canals 12
13 Ampulla Cupula Crista ampullaris Hair cells 13 _of_hearing.htm
14 Linear acceleration Utricle: แนวด ง Saccule: แนวราบ Otolithic membrane Calcium carbonate Hair cells Utricle & Saccule 14
15 Cochlear nerve Cochlear nuclei Auditory cortex Central auditory system 15
16 Vestibular nerve Vestibular nuclei Cerebellum Cerebral cortex Central vestibular system 16
17 Common Hearing and Balance Disorders External ear Middle ear Inner ear Pathology Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology Etiology Principle for diagnosis
18 Common Hearing and Balance Disorders External ear Middle ear Conductive hearing loss (CHL) Otalgia Otorrhea Inner ear Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) Vertigo Tinnitus
19 Common Hearing and Balance Disorders External ear
20 Common diseases of the external ear Pre-auricular sinus/ cyst ข ห อ ดต น ส งแปลกปลอมในช องห ช องห ต บ ห ช นนอกอ กเสบ การต ดเช อง สว ดบร เวณห 20
21 Pathology: ร เป ดเล ก ๆ หน าห ใต ต อ crus of helix Pre-auricular sinus/ cyst 21
22 Pre-auricular sinus/ cyst Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: hillock of His ท 1-3 มาจาก branchial arch ท 1 -> tragus, crus of helix และ helix hillock of His ท 4-6 มาจาก branchial arch ท 2 -> crura of antihelix, antihelix และ antitragus 22
23 Pre-auricular sinus/ cyst Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: epithelium ระหว าง hillock of His ท 1 และ 2 ไม สลายไป 23
24 Pre-auricular sinus/ cyst Etiology: congenital Principle for diagnosis: Preauricular pit Epithelium debris Recurrent infection 24
25 Impacted cerumen Pathology: 25
26 Impacted cerumen Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Ceruminous gland Epithelial migration 0.07 mm/day Aging: dry, decreased migration Etiology: แคะห Principle for diagnosis: CHL, ear wax, otalgia after swimming 26
27 Pathology: Foreign body in the ear canal 27
28 Foreign body in the ear canal Etiology: ใส เอง อ บ ต เหต Principle for diagnosis: Foreign body CHL, Otalgia, Otorrhea 28
29 Ear canal stenosis Pathology: 29
30 Ear canal stenosis Etiology: Congenital (congenital aural atresia) Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Failure of development of Branchial arch ท 1, 2, hillocks of His Canalization (ectodermal branchial groove) Principle for diagnosis: atresia, CHL, facial paralysis 30
31 Ear canal stenosis Etiology: Acquired trauma (temporal bone fracture) Principle for diagnosis: Bloody/ CSF otorrhea, CHL, facial paralysis 31
32 Temporal bone fracture Left complete facial paralysis ได ร บอน ญาตจากผ ป วยให ใช ภาพถ ายนาเสนอในทางว ชาการแล ว 32
33 Temporal bone fracture Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: fracture, bone chip Facial nerve 33
34 Ear canal stenosis Etiology: Acquired otitis externa; ป นห บ อย ๆ Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Chronic inflammatory stage Thick skin 34
35 Otitis externa Pathology: 35
36 Otitis externa Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Apopilosebaceous unit (hair follicles, sebaceous glands, ceruminous glands) Self-cleansing mechanism skin/cerumen protective barrier แคะห น าเข าห โรคผ วหน งท เก ดในช องห แพ ยาหยอดห 36
37 Otitis externa 3 stages: 1. preinflammatory: stratum corneum swelling, obstruction of apopilosebaceous unit 2. acute inflammatory: disruption of epithelium, ear canal swelling, otalgia, otorrhea 3. chronic inflammatory: eczematization, lichenification, superficial ulceration, itching 37
38 Otitis externa Etiology: Bacteria Fungus Acute otitis externa Principle for diagnosis: Otalgia, otorrhea, CHL Bullous myringitis Otomycosis 38 content/uploads/2013/03/acute-otitis-media.jpg
39 Herpes zoster oticus Pathology: Group of vesicles in sensory dermatome Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Reactivation of virus in sensory ganglion Immunocompromised host Etiology: Herpes (varicella) zoster virus 39
40 Ramsey Hunt syndrome Principle for diagnosis: vesicles in the head and neck area & facial paralysis 40
41 Common Hearing and Balance Disorders Middle ear
42 Common diseases of the middle ear ห ช นกลางอ กเสบ ห นป นเกาะฐานกระด กโกลน การบาดเจ บจากแรงด นต อห 42
43 Otitis media Pathology: Inflammation of the middle ear & mastoid Acute otitis media Otitis media With effusion Chronic otitis media 43
44 Otitis media Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Eustachian tube dysfunction: Pressure/ reflux/ drainage Anatomical obstruction: mucosal swelling, nasopharyngeal mass Functional obstruction: cleft palate, cartilage stiffness 44
45 Otitis media Etiology: bacteria AOM: - Streptococcus pneumonia - Haemophilus influenzae - Moraxella catarrhalis COM: - Proteus spp. - Pseudomonas aeruginosa - Staphylococcus spp. 45
46 Otitis media Principle for diagnosis: Otoscopy Otalgia CHL Otorrhea CHL Vertigo/ complications CHL Otorrhea 46
47 Otosclerosis Pathology: replacement of otic capsule with densed mineralized bone (otospongiosis) Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: osteoblastic & osteoclastic activity at stapes footplate Etiology: unknown, autosomal dominant Principle for diagnosis: CHL, Schawartze sign 47
48 Otitic barotrauma Pathology: different pressure between middle ear & environment -> swelling of middle ear mucosa, mucous gland secretion, tear of vessels Etiology: air travel, diving Principle for diagnosis: CHL, otalgia 48
49 Otitic barotrauma Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Boyle s law
50 Common Hearing and Balance Disorders Inner ear
51 Common diseases of the inner ear ห นป นในห ช นในหล ด โรคน าในห ไม เท าก น ประสาทห เส อมเฉ ยบพล นแบบไม ทราบสาเหต ห ช นในอ กเสบ เส นประสาททรงต วอ กเสบ ยาท เป นพ ษต อห การส ญเส ยการได ย นจากเส ยงด ง ห ต งเหต ส งอาย 51
52 Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo Most common cause of vertigo Pathology: floating of calcium carbonate crystal (otolith) in semicircular canal (canalithiasis), *posterior canal* Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Head movement -> canalith movement -> endolymph flow -> stimulation canalith 52
53 Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo Etiology: unknown, minor head trauma, common cold Principle for diagnosis: brief episodes of vertigo while changing positions *Dix-Hallpike test: vertigo & nystagmus 53
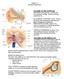
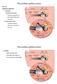
54 Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo Dix-Hallpike test: head turn 45 o, downward 30 o Test the right posterior semicircular canal: turn right ได ร บอน ญาตจากผ ป วยให ใช ภาพถ ายนาเสนอในทางว ชาการแล ว 54
55 Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo Dix-Hallpike test: positive; right ear Rotatory upbeating nystagmus downward to the right ear ได ร บอน ญาตจากผ ป วยให ใช ภาพถ ายนาเสนอในทางว ชาการแล ว 55
56 Ménière's disease; 2 nd most common cause of vertigo Idiopathic endolymphatic hydrops Pathology: Hydrops of the endolymph Etiology: idopathic 56
57 Ménière's disease; Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: **Rupture of membranous labyrinth -> mixing of endolymph & periplymph -> acute inactivation of nerve cells -> auditory & vestibular neuronal outflow -> ATTACK! Principle for diagnosis: triad of vertigo, SNHL, tinnitus 57
58 Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss Pathology: nonspecific Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: hypothesis 1) viral infection 2) cochlear ischemia, perilymphatic oxygen 3) intracochlear membrane rupture 4) autoimmune inner ear disease 5) CNS anomalies Etiology: idiopathic Principle for diagnosis: Sudden loss of hearing < 3 days audiogram: PTA > 30 dbhl, 3 frequencies 58
59 Labyrinthitis Pathology: depended on causes of infection Scala tympani filled with a mixture of acute inflammatory cells, bacteria, and a granular eosinophilic precipitate Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Suppurative labyrinthitis From middle ear: via round window, fistula From CSF: via internal acoustic canal, cochlear modiolus, cochlear duct 59
60 Labyrinthitis Etiology: 1. Bacteria: Otitis media Meningitis: Streptococcus pneumonia, Haemophilus influenzae, Neiseria meningitides, Streptococcus suis 2. Virus: herpes simplex type I, herpes zoster, cytomegalovirus 3. spirochete: syphilis 4. mycobacterium Principle for diagnosis: SNHL, vertigo, specific symptoms 60
61 Vestibular neuritis Vestibular neuronitis Pathology: degeneration in scarpa ganglion, chronic inflammation Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: hypofunction Etiology:? reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus type I in vestibular ganglion Principle for diagnosis: vertigo (days), no hearing loss, common cold 61
62 Ototoxicity Pathology: depended on group cochlear hair cells; base -> apex, Outer hair cells sensitive > inner hair cells Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: blood-labyrinth barrier Severity: multiple groups, high dose, extreme age Principle for diagnosis: SNHL, vertigo, tinnitus 62
63 Noise-induced hearing loss ความด งของเส ยงในส งแวดล อม ป จจ ยท ม ผลกระทบต อการได ย น ความด ง ความถ ล กษณะเส ยง ระยะเวลาส มผ สเส ยง สภาพห 63
64 Noise-induced hearing loss ชน ดและแหล งกาเน ดเส ยง 1. เส ยงด งสม าเสมอ (Steady state Noise): เคร องจ กร เคร องทอผ า 2. เส ยงด งค อยสล บไปมา (Fluctuation): เล อยไฟฟ า หวอ 3. เส ยงท ด งเป นระยะ (Intermittent Noise): การจราจร เคร องบ น 4. เส ยงกระแทก (Impulse Noise or Impact Noise): ป น ประท ด 64 ไพฑ รย น กสอน อ นตรายจากเส ยงด ง ใน: พ ช ต ส ทธ ไตรย, สายสวาท ไชยเศรษฐ, ส ว ชา อ ศราด ส ยก ล, บรรณาธ การ. ตาราห คอ จม ก สาหร บเวชปฏ บ ต ท วไป ภาคว ชาโสต ศอ นาส กว ทยา ค ณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม. Trick think; หน า
65 Pathology: Noise-induced hearing loss เส ยงด งสม าเสมอ (Steady state Noise): เคร องจ กร เคร องทอผ า Damage organ of Corti: 1 st = OHCs: fused sterocilia 65
66 Noise-induced hearing loss 2 nd = IHCs, supporting cells; 3 rd = Entire organ of Corti Swelling auditory nerve ending, degeneration of synapse in cochlear nucleus 66
67 Noise-induced hearing loss Pathology: เส ยงกระแทก (Impulse Noise or Impact Noise): ป น ประท ด Rupture of membrane in organ of Corti Mixing of endolymph & perilymph Tympanic membrane rupture 67
68 Noise-induced hearing loss Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: Acoustic reflex: > 90 db contracted of stapedius muscle Not function if noise < 1 seconds, > 140 decibels Principle for diagnosis: SNHL 3-6 khz), tinnitus 68
69 Presbycusis Age-related hearing loss Pathology: sensory cells & supporting cells in organ of Corti, spiral ganglion cells atrophy of stria vascularis, basilar membrane stiffness Pathogenesis/ Pathophysiology: multifactorial Etiology: older, vascular disease, ototoxic, noise, smoking Principle for diagnosis: bilateral SNHL, > year-old 69
70 ระด บของความผ ดปกต ของการได ย น และความสามารถในการฟ ง
71 ระด บของความผ ดปกต ของการได ย น และความสามารถในการฟ ง ระด บของการได ย น ห ปกต (normal hearing) ห ต งน อย (mild hearing loss) ห ต งปานกลาง (moderate hearing loss) ห ต งมาก (moderately severe hearing loss) Hearing threshold ความสามารถในการฟ ง (pure tone average) -10 ถ ง 25 เดซ เบล ไม ลาบากในการร บฟ งคาพ ด เดซ เบล ไม ได ย นเส ยงพ ดเบา ๆ เดซ เบล พอจะเข าใจในระด บความด งปกต ระยะ 3-5 ฟ ต เดซ เบล ต องพ ดด วยเส ยงด ง ๆ จ งจะเข าใจ แต จะม ความ ลาบากในการฟ งเม ออย ท ม เส ยงจอแจ ห ต งอย างร นแรง เดซ เบล อาจจะได ย นเส ยงตะโกน ในระยะ 1 ฟ ต (severe hearing loss) แต ไม เข าใจ ห หนวก (deafness) > 90 เดซ เบล เส ยงตะโกนก ไม ได ย น 71
72 ห ปกต (Normal limits) -10 ถ ง 25 db ไม ลาบากในการร บฟ งเส ยงพ ด ห ต งน อย (Mild hearing loss) db ไม ได ย นเส ยงพ ดเบาๆ ระด บของการได ย น วาสนา วะส นนท การฟ นฟ สมรรถภาพการได ย น ใน: พ ช ต ส ทธ ไตรย, สายสวาท ไชยเศรษฐ, ส ว ชา อ ศราด ส ยก ล, บรรณาธ การ. ตาราห คอ จม ก สาหร บเวชปฏ บ ต ท วไป ภาคว ชาโสต ศอ นาส กว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม. Trick think; หน า
73 ระด บของการได ย น ห ต งปานกลาง (Moderate hearing loss) db ** พ ดด วยความด งปกต แล วไม ได ย น ห ต งมาก (Moderately severe hearing loss) db ต องพ ดด วยเส ยงด งๆ จ งจะเข าใจ และเม ออย ท ม เส ยงจอแจ จะม ความลาบากในการฟ ง วาสนา วะส นนท การฟ นฟ สมรรถภาพการได ย น ใน: พ ช ต ส ทธ ไตรย, สายสวาท ไชยเศรษฐ, ส ว ชา อ ศราด ส ยก ล, บรรณาธ การ. ตาราห คอ จม ก สาหร บเวชปฏ บ ต ท วไป ภาคว ชาโสต ศอ นาส กว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม. Trick think; หน า
74 ระด บของการได ย น ห ต งอย างร นแรง (Severe hearing loss) db ตะโกนหร อใช เคร องขยายเส ยง จ งจะได ย น แต ย งได ย นไม ช ดด วย ห หนวก (Deafness) > 90 db ตะโกนหร อขยาย เส ยงพ ดแล ว ก ย งไม ได ย น ไม เข าใจ วาสนา วะส นนท การฟ นฟ สมรรถภาพการได ย น ใน: พ ช ต ส ทธ ไตรย, สายสวาท ไชยเศรษฐ, ส ว ชา อ ศราด ส ยก ล, บรรณาธ การ. ตาราห คอ จม ก สาหร บเวชปฏ บ ต ท วไป ภาคว ชาโสต ศอ นาส กว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม. Trick think; หน า
75 Suggested resources 75
76 Suggested resources 2. Physiology of hearing: phiz/classes_stud/en/nurse/bacchaour%20of%20sciences%2 0in%20nurses/ADN/18_Physiology_of_hearing.htm 3. Ear anatomy: 76
77
Anatomy of the Ear Region. External ear Middle ear Internal ear
 Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! Chapter 17 Part 2 Special Senses! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Ear. Utricle & saccule in the vestibule Connected to each other and to the endolymphatic sac by a utriculosaccular duct
 Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
AUDITORY APPARATUS. Mr. P Mazengenya. Tel 72204
 AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
The Ear. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
What is the effect on the hair cell if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium?
 CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
Assessing the Deaf & the Dizzy. Phil Bird Senior Lecturer University of Otago, Christchurch Consultant Otolaryngologist CPH & Private
 Assessing the Deaf & the Dizzy Phil Bird Senior Lecturer University of Otago, Christchurch Consultant Otolaryngologist CPH & Private Overview Severe & profoundly deaf children & adults Neonatal screening
Assessing the Deaf & the Dizzy Phil Bird Senior Lecturer University of Otago, Christchurch Consultant Otolaryngologist CPH & Private Overview Severe & profoundly deaf children & adults Neonatal screening
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium
 Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Anatomy of the ear: Lymphatics
 Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
The Prevalence of Detectable Blood Alcohol Concentration among Unnatural Deaths in Northern Thailand
 The Prevalence of Detectable Blood Alcohol Concentration among Unnatural Deaths in Northern Thailand Siripun Narongchai MSc*, Paitoon Narongchai MD* * Department of Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine,
The Prevalence of Detectable Blood Alcohol Concentration among Unnatural Deaths in Northern Thailand Siripun Narongchai MSc*, Paitoon Narongchai MD* * Department of Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine,
A&P 1. Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab. Basic Concepts. Pre-lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts Pre-lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE: these notes do not follow the order
A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts Pre-lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE: these notes do not follow the order
Chapter 1: Applied Anatomy, Physiology and Embryology of the Ear. Anatomy and Physiology. The Outer Ear. The Pinna. The External Ear Canal
 Chapter 1: Applied Anatomy, Physiology and Embryology of the Ear The ear contains two specialized sensory organs, the cochlea and the vestibular apparatus, enclosed in the extremely hard protective casing
Chapter 1: Applied Anatomy, Physiology and Embryology of the Ear The ear contains two specialized sensory organs, the cochlea and the vestibular apparatus, enclosed in the extremely hard protective casing
A&P 1. Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab. Basic Concepts. These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab
 A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE:
A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE:
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals Gelatinous mass. Cilia. Hair cells. Vestibular nerve. Vestibular ganglion
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Acquired Deafness Loss of hearing that occurs or develops sometime in the course of a lifetime, but is not present at birth.
 Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
Sasan Dabiri, MD, Assistant Professor
 Sasan Dabiri, MD, Assistant Professor Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences October 2015 Outlines Anatomy of Vestibular System
Sasan Dabiri, MD, Assistant Professor Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences October 2015 Outlines Anatomy of Vestibular System
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
Vestibular physiology
 Vestibular physiology 2017 Utricle A flat epithelium: horizontal in the upright head Utricle Hair cells: no axons hair cells Utricle Hair cells synapse onto 8th nerve afferents. 8th nerve afferents Hair
Vestibular physiology 2017 Utricle A flat epithelium: horizontal in the upright head Utricle Hair cells: no axons hair cells Utricle Hair cells synapse onto 8th nerve afferents. 8th nerve afferents Hair
Scrub In. What is the function of cerumen? Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal?
 Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Hearing. By Jack & Tori
 Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
The ear: some applied basic science
 Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
ICD10 CODES CODE DESCRIPTION R Abnormal auditory function study H Abnormal auditory perception, bilateral H Abnormal auditory
 ICD10 CODES CODE DESCRIPTION R94.120 Abnormal auditory function study H93.293 Abnormal auditory perception, bilateral H93.292 Abnormal auditory perception, left ear H93.291 Abnormal auditory perception,
ICD10 CODES CODE DESCRIPTION R94.120 Abnormal auditory function study H93.293 Abnormal auditory perception, bilateral H93.292 Abnormal auditory perception, left ear H93.291 Abnormal auditory perception,
Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS
 Hearing loss Overview Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Not deafness Deaf is a total lack of hearing Deafness
Hearing loss Overview Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Not deafness Deaf is a total lack of hearing Deafness
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Management of Ear, Hearing and Balance Disorders: Fact, Fiction, and Future
 Management of Ear, Hearing and Balance Disorders: Fact, Fiction, and Future George W. Hicks, M,D. 7440 N. Shadeland Avenue, Suite 150 Indianapolis, IN 46250 904 N. Samuel Moore Parkway Mooresville, IN
Management of Ear, Hearing and Balance Disorders: Fact, Fiction, and Future George W. Hicks, M,D. 7440 N. Shadeland Avenue, Suite 150 Indianapolis, IN 46250 904 N. Samuel Moore Parkway Mooresville, IN
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D.
 Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
1. GOAL 2. OBJECTIVES a) KNOWLEDGE b) SKILLS c) INTEGRATION
 1. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Otorhinolaryngology is that the undergraduate student have acquired adequate knowledge and skills for optimally dealing with common disorders
1. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Otorhinolaryngology is that the undergraduate student have acquired adequate knowledge and skills for optimally dealing with common disorders
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist
 WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
Section 1 EAR. Section Outlines
 Section 1 EAR Section Outlines Development of the Ear Anatomy of the Ear Physiology of the Ear History Taking with Symptomatology of Ear Diseases Examination of the Ear Congenital Diseases of the External
Section 1 EAR Section Outlines Development of the Ear Anatomy of the Ear Physiology of the Ear History Taking with Symptomatology of Ear Diseases Examination of the Ear Congenital Diseases of the External
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST
 www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The cochlea: auditory sense. The cochlea: auditory sense
 Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
CITY & HACKNEY PATHFINDER CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP. Vertigo. (1) Vertigo. (4) Provisional Diagnosis. (5) Investigations. lasting days or weeks
 Authors: Dr Lucy O'Rouke and Mr N Eynon-Lewis Review date: January 2017 Vertigo (1) Vertigo (2) History (3) Examination (4) Provisional Diagnosis (5) Investigations (6) Medical Cause (7) Psychiatric Cause
Authors: Dr Lucy O'Rouke and Mr N Eynon-Lewis Review date: January 2017 Vertigo (1) Vertigo (2) History (3) Examination (4) Provisional Diagnosis (5) Investigations (6) Medical Cause (7) Psychiatric Cause
Result of Ambulatory Diet Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
 Result of Ambulatory Diet Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prasert Sunsaneevithayakul MD*, Sujin Kanokpongsakdi MD*, Anuwat Sutanthavibul MD*, Pornpimol Ruangvutilert MD, PhD*, Dittakarn Boriboohirunsarn
Result of Ambulatory Diet Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prasert Sunsaneevithayakul MD*, Sujin Kanokpongsakdi MD*, Anuwat Sutanthavibul MD*, Pornpimol Ruangvutilert MD, PhD*, Dittakarn Boriboohirunsarn
INFECTION OF EXTERNAL EAR. Miguel G. Wagner R1 HUSE 2017
 INFECTION OF EXTERNAL EAR Miguel G. Wagner R1 HUSE 2017 ANATOMY AURICLE + EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL (EAC) + EPITELIAL SURFACE TYMPANIC MB Auricle Fibroelastic cartilage (except lobule) + perichondrium +
INFECTION OF EXTERNAL EAR Miguel G. Wagner R1 HUSE 2017 ANATOMY AURICLE + EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL (EAC) + EPITELIAL SURFACE TYMPANIC MB Auricle Fibroelastic cartilage (except lobule) + perichondrium +
Outcome of Myringotomy with Ventilation Tube for Otitis Media with Effusion in Thai Children: Ramathibodi Experiences
 Preliminary Report Outcome of Myringotomy with Ventilation Tube for Otitis Media with Effusion in Thai Children: Ramathibodi Experiences Kunchitthape Tanpowpong MD*, Intuorn Saisukul MD*, Hataikorn Kittimanont
Preliminary Report Outcome of Myringotomy with Ventilation Tube for Otitis Media with Effusion in Thai Children: Ramathibodi Experiences Kunchitthape Tanpowpong MD*, Intuorn Saisukul MD*, Hataikorn Kittimanont
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 11 Ακουστικό και Αιθουσιαίο Σύστημα (Auditory and Vestibular Systems) Introduction Sensory Systems Sense of
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 11 Ακουστικό και Αιθουσιαίο Σύστημα (Auditory and Vestibular Systems) Introduction Sensory Systems Sense of
Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease
 Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura President The Society for Promotion of International Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Tokyo, Japan
Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura President The Society for Promotion of International Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Tokyo, Japan
DIZZINESS Varieties. : Fainting, hypotension : Rotatory, spinning. : Muscular incoordination : Collapse without LOC: ELH : Disturbed awareness
 DIZZINESS Varieties head Syncope Vertigo Dysequilibrium Ataxia Drop attacks Confusion Panic Attacks Non-organic : Fainting, hypotension : Rotatory, spinning : Unsteadiness on moving : Muscular incoordination
DIZZINESS Varieties head Syncope Vertigo Dysequilibrium Ataxia Drop attacks Confusion Panic Attacks Non-organic : Fainting, hypotension : Rotatory, spinning : Unsteadiness on moving : Muscular incoordination
Complications of otitis media
 Chronic otitis media Definition:- Complications of otitis media Otitis media (OM) is broadly defined as inflammation from any cause of the middle ear.this may involve any of the contiguous pneumatized
Chronic otitis media Definition:- Complications of otitis media Otitis media (OM) is broadly defined as inflammation from any cause of the middle ear.this may involve any of the contiguous pneumatized
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Age Related Changes in Hearing Level among Thai People
 Age Related Changes in Hearing Level among Thai People Orawan Kaewboonchoo PhD*, Sumlee Saleekul MSc**, Suchart Jaipukdee MEd*** * Department of Public Health Nursing, Faculty of Public Health, Mahidol
Age Related Changes in Hearing Level among Thai People Orawan Kaewboonchoo PhD*, Sumlee Saleekul MSc**, Suchart Jaipukdee MEd*** * Department of Public Health Nursing, Faculty of Public Health, Mahidol
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Arastoo Vossough, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiology
 Disorders of the Temporal Bone Arastoo Vossough, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiology 1st Branchial Cleft Cyst Remnant of 1 st branchial apparatus Rare Cystic lesions: I- around pinna II- connecting
Disorders of the Temporal Bone Arastoo Vossough, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiology 1st Branchial Cleft Cyst Remnant of 1 st branchial apparatus Rare Cystic lesions: I- around pinna II- connecting
Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders
 Health Reference Series Second Edition Basic Consumer Health Information about Disorders of the Ears, Hearing Loss, Vestibular Disorders, Nasal and Sinus Problems, Throat and Vocal Cord Disorders, and
Health Reference Series Second Edition Basic Consumer Health Information about Disorders of the Ears, Hearing Loss, Vestibular Disorders, Nasal and Sinus Problems, Throat and Vocal Cord Disorders, and
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
HEARING IMPAIRMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Divisions of the Ear. Inner Ear. The inner ear consists of: Cochlea Vestibular
 HEARING IMPAIRMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Recognize the clinical manifestation and to be able to request appropriate investigations Interpret lab investigations for basic management.
HEARING IMPAIRMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Recognize the clinical manifestation and to be able to request appropriate investigations Interpret lab investigations for basic management.
Chronic Ear Disease. Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09
 Chronic Ear Disease Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09 ETD URIs Viral-induced damage to ET lining resulting in decreased mucociliary clearance Viral invasion of ME mucosa results in inflamm Reflux
Chronic Ear Disease Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09 ETD URIs Viral-induced damage to ET lining resulting in decreased mucociliary clearance Viral invasion of ME mucosa results in inflamm Reflux
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Vertigo. Definition Important history questions Examination Common vertigo cases and management Summary
 Vertigo Vertigo Definition Important history questions Examination Common vertigo cases and management Summary Cases 1) 46 year old man presents two weeks after knocking his head with recurrent episodes
Vertigo Vertigo Definition Important history questions Examination Common vertigo cases and management Summary Cases 1) 46 year old man presents two weeks after knocking his head with recurrent episodes
Unit # 10 B Assessment of Ears
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY KARACHI) Unit # 10 B Assessment of Ears Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN, MScN (Std. DUHS) Instructor New Life College of Nursing Updated, January
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY KARACHI) Unit # 10 B Assessment of Ears Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN, MScN (Std. DUHS) Instructor New Life College of Nursing Updated, January
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Special Senses. Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition)
 Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Anatomy and Pathophysiology for ICD-10 Module 11. Ear and Mastoid
 Anatomy and Pathophysiology for ICD-10 Module 11 Ear and Mastoid Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Ear Flap (Pinna) Ear Canal (Meatus) Middle Ear Tympanic Membrane (Eardrum) Hammer (Malleus) Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Pathophysiology for ICD-10 Module 11 Ear and Mastoid Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Ear Flap (Pinna) Ear Canal (Meatus) Middle Ear Tympanic Membrane (Eardrum) Hammer (Malleus) Anatomy and Physiology
Vestibular Function and Anatomy. UTMB Grand Rounds April 14, 2004 Gordon Shields, MD Arun Gadre, MD
 Vestibular Function and Anatomy UTMB Grand Rounds April 14, 2004 Gordon Shields, MD Arun Gadre, MD System of balance Membranous and bony labyrinth embedded in petrous bone 5 distinct end organs 3 semicircular
Vestibular Function and Anatomy UTMB Grand Rounds April 14, 2004 Gordon Shields, MD Arun Gadre, MD System of balance Membranous and bony labyrinth embedded in petrous bone 5 distinct end organs 3 semicircular
Krittin Silanun MD, MSc*, Naesinee Chaiear MD, MMedSc, Ph D*, Wipa Rechaipichitkul MD**
 Prevalence of Silicosis in Stone Carving Workers Being Exposed to Inorganic Dust at Sikhiu District Nakhonratchasima Province, Thailand; Preliminary Results Krittin Silanun MD, MSc*, Naesinee Chaiear MD,
Prevalence of Silicosis in Stone Carving Workers Being Exposed to Inorganic Dust at Sikhiu District Nakhonratchasima Province, Thailand; Preliminary Results Krittin Silanun MD, MSc*, Naesinee Chaiear MD,
Disclosure! Torphong(Bunmaprasert,(MD.(
 PRINCIPLE(OF(SURGICAL(TREATMENT( IN(DEGENERATIVE(LUMBAR(DISEASES( รศ.นพ.ต อพงษ บ ญ The$7 th $CMU$Neurosurgery$Forum$$ December$11 มาประเสร ฐ th,$2015! หน วยโรคกระด กส นหล ง ภาคว ชาออร โทป ด กส คณะแพทยศาสตร
PRINCIPLE(OF(SURGICAL(TREATMENT( IN(DEGENERATIVE(LUMBAR(DISEASES( รศ.นพ.ต อพงษ บ ญ The$7 th $CMU$Neurosurgery$Forum$$ December$11 มาประเสร ฐ th,$2015! หน วยโรคกระด กส นหล ง ภาคว ชาออร โทป ด กส คณะแพทยศาสตร
เน องอก (Neoplasm) ห วข อบรรยาย. Neoplasia. Neoplasia. Benign and Malignant tumors
 30 พฤศจ กายน พ.ศ. 2553 เน องอก (Neoplasm) นายแพทย ดร. ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยาและน ต เวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร ห วข อบรรยาย ความหมายของเน องอก และชน ดของเน องอก ความแตกต างระหว
30 พฤศจ กายน พ.ศ. 2553 เน องอก (Neoplasm) นายแพทย ดร. ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยาและน ต เวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร ห วข อบรรยาย ความหมายของเน องอก และชน ดของเน องอก ความแตกต างระหว
J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat
 J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat Reading excerpt Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat of J.P.S. Bakshi Publisher: B. Jain http://www.narayana-publishers.com/b5603 Copying excerpts is not permitted.
J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat Reading excerpt Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat of J.P.S. Bakshi Publisher: B. Jain http://www.narayana-publishers.com/b5603 Copying excerpts is not permitted.
Vertigo: A practical approach to diagnosis and treatment. John Waterston
 Vertigo: A practical approach to diagnosis and treatment John Waterston Background. Vertigo is a symptom that has diverse causes. The diagnosis may remain elusive even after exhaustive clinical enquiry
Vertigo: A practical approach to diagnosis and treatment John Waterston Background. Vertigo is a symptom that has diverse causes. The diagnosis may remain elusive even after exhaustive clinical enquiry
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
 Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome Teeradej Kuptanon, MD Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University PP; เด กหญ งไทย อาย 8 ป กทม. ประว ต จาก มารดา CC หายใจหอบเหน อยตอนกลางค
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome Teeradej Kuptanon, MD Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University PP; เด กหญ งไทย อาย 8 ป กทม. ประว ต จาก มารดา CC หายใจหอบเหน อยตอนกลางค
Imaging of Hearing Loss
 Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Acoustic Rhinometry Evaluation in Allergic Rhinitis Patients before and after Turbinate Radiofrequency Ablation
 Acoustic Rhinometry Evaluation in Allergic Rhinitis Patients before and after Turbinate Radiofrequency Ablation Girapong Ungkhara MD*, Pichai Purpermpulsiri MD* * Department of Otolaryngology, BMA Medical
Acoustic Rhinometry Evaluation in Allergic Rhinitis Patients before and after Turbinate Radiofrequency Ablation Girapong Ungkhara MD*, Pichai Purpermpulsiri MD* * Department of Otolaryngology, BMA Medical
ﺎﻨﺘﻤﻠﻋ ﺎﻣ ﻻا ﺎﻨﻟ ﻢﻠﻋ ﻻ ﻚﻧﺎﺤﺒﺳ اﻮﻟﺎﻗ ﻢﻴﻜﺤﻟا ﻢﻴﻠﻌﻟا ﺖﻧأ ﻚﻧا ﻢﻴﻈﻌﻟا ﷲا قﺪﺻ HEARING LOSS
 قالوا سبحانك لا علم لنا الا ما علمتنا انك أنت العليم الحكيم صدق االله العظيم HEARING LOSS 1 Hearing loss: Deviation from normal hearing in one or both ears. Hearing handicap: This term refers to total
قالوا سبحانك لا علم لنا الا ما علمتنا انك أنت العليم الحكيم صدق االله العظيم HEARING LOSS 1 Hearing loss: Deviation from normal hearing in one or both ears. Hearing handicap: This term refers to total
Basic plastic surgery and wound management นพ.โอภาส พ ณไชย หน วยศ ลยศาสตร ตกแต ง ภาคว ชาศ ลยศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม ก ภาพ นธ 2562
 Basic plastic surgery and wound management นพ.โอภาส พ ณไชย หน วยศ ลยศาสตร ตกแต ง ภาคว ชาศ ลยศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม ก ภาพ นธ 2562 ว ตถ ประสงค ม ความเข าใจความร พ นฐานทางศ ลยศาสตร ตกแต ง
Basic plastic surgery and wound management นพ.โอภาส พ ณไชย หน วยศ ลยศาสตร ตกแต ง ภาคว ชาศ ลยศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม ก ภาพ นธ 2562 ว ตถ ประสงค ม ความเข าใจความร พ นฐานทางศ ลยศาสตร ตกแต ง
Diseases of External Ear. Hassan El Ibiary
 Diseases of External Ear Hassan El Ibiary Developmental Anatomy Pinna is formed of 3 tubercles from the first branchial arch and 3 from second arch. They fuse forming adult appearance in week 20. EAC is
Diseases of External Ear Hassan El Ibiary Developmental Anatomy Pinna is formed of 3 tubercles from the first branchial arch and 3 from second arch. They fuse forming adult appearance in week 20. EAC is
Peripheral vestibular disorders will affect 1 of 13 people in their lifetime
 Peripheral vestibular disorders will affect 1 of 13 people in their lifetime 80% of affected persons seek medical consultation Unclear how many of these are for peripheral vs central disorders Generally:
Peripheral vestibular disorders will affect 1 of 13 people in their lifetime 80% of affected persons seek medical consultation Unclear how many of these are for peripheral vs central disorders Generally:
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION
 SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
บทค ดย อ : ภาวะเม ดเล อดแดงมากในผ ป วยอาย น อย
 Polycythemia in the Young Insiripong S Yingsitsiri W Boondumrongsagul J Hematology Unit, Department of Medicine, Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital, Mueang Nakhon Ratchasima, Nakhon Ratchasima, 30000 (E-mail
Polycythemia in the Young Insiripong S Yingsitsiri W Boondumrongsagul J Hematology Unit, Department of Medicine, Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital, Mueang Nakhon Ratchasima, Nakhon Ratchasima, 30000 (E-mail
Laith Sorour. Facial nerve (vii):
 Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Cholesteatoma and Non-cholesteatomatous Inflammatory Disease. Cholesteatoma. Disclosures. Overview EAC. Cholesteatoma. None
 Disclosures Cholesteatoma and Non-cholesteatomatous Inflammatory Disease None Amy F Juliano, MD Staff Radiologist, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Assistant Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical
Disclosures Cholesteatoma and Non-cholesteatomatous Inflammatory Disease None Amy F Juliano, MD Staff Radiologist, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Assistant Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical
The Senses. Chapter 10 7/8/11. Introduction
 Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Histology of Ear. Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008
 Histology of Ear Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008 References: Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Color textbook of histology. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia. WB Saunders company. 2001 Kierszenbaum
Histology of Ear Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008 References: Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Color textbook of histology. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia. WB Saunders company. 2001 Kierszenbaum
Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems
 Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned
Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned
OBJECTIVES BALANCE EVALUATION COMMON CAUSES OF BALANCE DEFICITS POST TBI BRAIN INJURY BALANCE RELATIONSHIP
 OBJECTIVES Understand variables that contribute to balance deficits Understand the relationship between a brain injury and balance Become familiar with the components of a vestibular/balance assessment
OBJECTIVES Understand variables that contribute to balance deficits Understand the relationship between a brain injury and balance Become familiar with the components of a vestibular/balance assessment
Is Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men a High Morbidity Surgery for Localized or Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer?
 Is Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men a High Morbidity Surgery for Localized or Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer? Sunai Leewansangtong MD*, Suchai Soontrapa MD*, Chaiyong Nualyong MD*, Sittiporn Srinualnad
Is Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men a High Morbidity Surgery for Localized or Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer? Sunai Leewansangtong MD*, Suchai Soontrapa MD*, Chaiyong Nualyong MD*, Sittiporn Srinualnad
Normal membranous labyrinth. Dilated membranous labyrinth in Meniere's disease (Hydrops)
 Meniere s Disease Normal membranous labyrinth Dilated membranous labyrinth in Meniere's disease (Hydrops) Normal membranous labyrinth Dilated membranous labyrinth in Meniere's disease (Hydrops) DEFINITION
Meniere s Disease Normal membranous labyrinth Dilated membranous labyrinth in Meniere's disease (Hydrops) Normal membranous labyrinth Dilated membranous labyrinth in Meniere's disease (Hydrops) DEFINITION
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism
 Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
9/7/2013. Ciprodex Webinar Leader. Off label Uses
 Alcon labs Ciprodex Webinar Leader Off label Uses Deena B Hollingsworth MSN, FNP-BC, CORLN ENT Specialists of Northern Virginia Falls Church, Virginia Examine common physiologic changes of aging Discuss
Alcon labs Ciprodex Webinar Leader Off label Uses Deena B Hollingsworth MSN, FNP-BC, CORLN ENT Specialists of Northern Virginia Falls Church, Virginia Examine common physiologic changes of aging Discuss
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM
 SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
Usefulness of an Abnormal Ankle-Brachial Index to Predict the Presence of Coronary Artery Disease
 Usefulness of an Abnormal Ankle-Brachial Index to Predict the Presence of Coronary Artery Disease Sittiluck Wongwantanee, MD, Damras Tresukosol, MD, and Kamol Udol MD Division of Cardiology, Faculty of
Usefulness of an Abnormal Ankle-Brachial Index to Predict the Presence of Coronary Artery Disease Sittiluck Wongwantanee, MD, Damras Tresukosol, MD, and Kamol Udol MD Division of Cardiology, Faculty of
Methods and technique of endoscopic research of ENTorgans. Clinical anatomy and. physiology of auditory analyzer. Study 1
 Methods and technique of endoscopic research of ENTorgans. Clinical anatomy and physiology of auditory analyzer Study 1 Auditory analyzer consists of: Auricle Middle ear Inner ear Peripheral Part Transmitting
Methods and technique of endoscopic research of ENTorgans. Clinical anatomy and physiology of auditory analyzer Study 1 Auditory analyzer consists of: Auricle Middle ear Inner ear Peripheral Part Transmitting
Control of eye movement
 Control of eye movement Third Nerve Palsy Eye down and out Trochlear Nerve Palsy Note: Right eye Instead of intorsion and depression action of superior oblique See extorsion and elevation Observe how
Control of eye movement Third Nerve Palsy Eye down and out Trochlear Nerve Palsy Note: Right eye Instead of intorsion and depression action of superior oblique See extorsion and elevation Observe how
